INNOVATION MATRIX
ARTICLE
Innovation is seen as the preferred tool to stay ahead of the competition, grow business and take advantage of new technologies.
Introduction
Innovation occupies a large place in our society and although it is important, it is often confused with the future. It is important to understand that not all innovation today necessarily has a place in the future, such is the very nature of innovation and the future, it can appear quickly or slowly and then suddenly. It is therefore important to understand that innovation does not guarantee the future, that it does not future-proof us, hence the importance of detecting signals of the future and, above all, of focusing on the customer in order to understand their future needs and desires. Innovation is therefore possible on each horizon, but its continuity is not necessarily assured on all.
That said, it is also important to know the types of innovations in order to orient oneself the right way and especially in order to noid avoid them because they may not have a huge impact in the present. Having lucidity in this regard is important.
Innovation inside the 3 Horizons
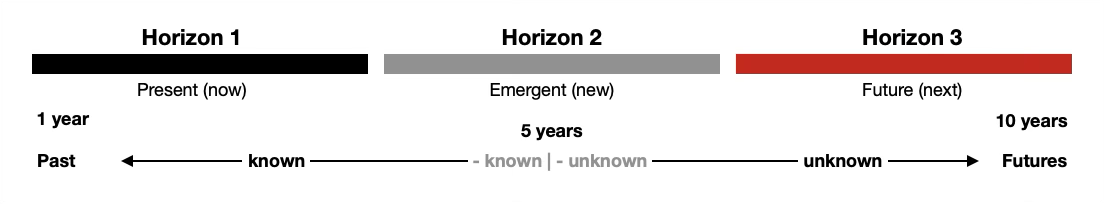
Innovation is a wide, deep and extremely interesting topic that may be a little difficult to summarize because innovation comes in very many shapes and colors. Speaking of colors, a good way to situate innovation is to use the 3 Horizons so we may see if an innovation is for now, next or something that will take years to develop before it is ready to be marketed. One practice that can help us make wins is to tinker with ideas along or within each horizons. This graphic can suggest a line or time line for this type of inquiry.
Innovation is a wide, deep and extremely interesting topic that may be a little difficult to summarize because innovation comes in very many shapes and colors. Speaking of colors, a good way to situate innovation is to use the 3 Horizons so we may see if an innovation is for now, next or something that will take years to develop before it is ready to be marketed. One practice that can help us make wins is to tinker with ideas along or within each horizons. This graphic can suggest a line or time line for this type of inquiry.
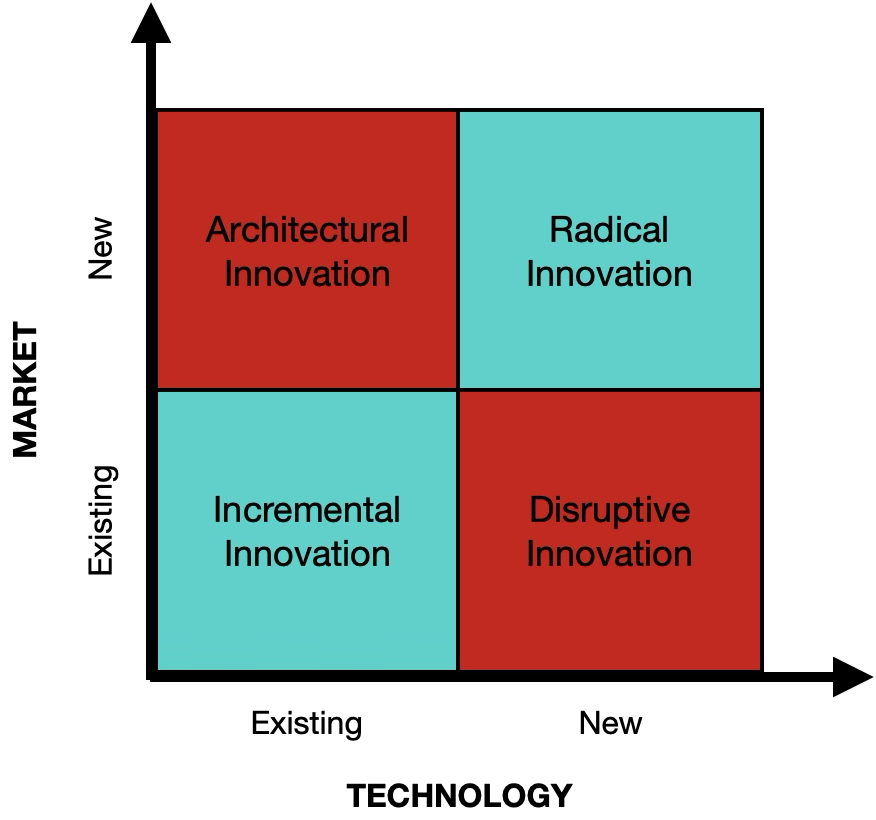
The 4 types of innovations
The 4 types of innovation (a classificatin attributed to the OECD) can be grouped under an innovation matrix that separates the types of innovation into four categories: architectural innovation, incremental or gradual innovation, disruptive innovation, and finally radical innovation. These categories can apply to product innovation, marketing innovation, technological innovation, or process innovation :
Architectural innovation refers to the use of existing technologies to create new products or services in order to develop new markets and/or new consumers who have never purchased this product/service before. For example, technologies used for carpooling, including geolocation, applied to taxi services.
Incremental innovation) refers to a series of small-scale improvements made to an existing product or service to add or maintain value.
Disruptive innovation is an idea that improves an existing market by surpassing the needs of a customer base, ultimately supplanting the old market.
Radical innovation destroys the current market and value network, creating a completely new one.
Schumpeter’s 5 types
Schumpeter elaborated his theory to describe the process of innovation and also distinguished five types of innovation: (1) new production processes, (2) new products, (3) new materials or resources, (4) new markets, as well as (5) new forms of organizations (The Theory of Economic Development, Schumpeter, 1934. Although probably less referred to they nonetheless represent relevant forms of innovations.
Utilization
For organization less familiar with innovation, utilizing the matrix or Schumpeter’s 5 types can be useful to better understand the types of innovations in order to situate oneself and to better understand the value that we can add in the targeted system or ecosystem and also to better direct collaboration, partnership and financing efforts.
N.B. Innovation is not necessarily the future
It is important to understand that innovation does not guarantee the future, that it does not future-proof us, hence the importance of detecting signals of the future and especially of focusing on the customer in order to understand their future needs and desires. Innovation is therefore possible on each horizon, but its continuity is not necessarily assured on all.